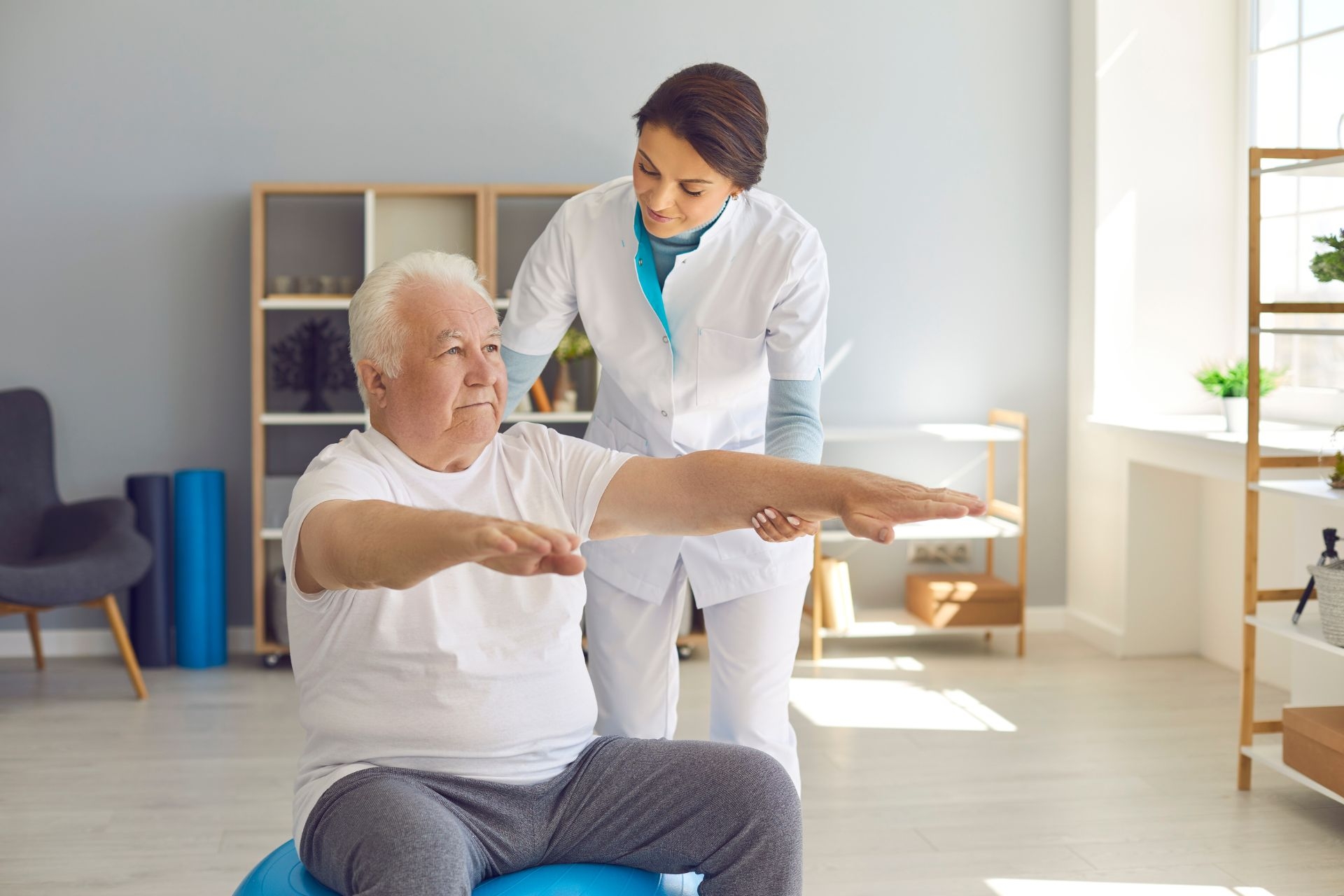


Sensory integration therapy is a type of therapy that aims to help individuals with sensory processing disorders by addressing difficulties in processing and responding to sensory information. It works by providing a controlled and structured environment where individuals can engage in activities that stimulate their senses in a therapeutic way. The therapy focuses on improving the brain's ability to process and integrate sensory information, leading to better overall functioning and behavior.
Pain ManagementThere are several signs and symptoms that may indicate a need for sensory integration therapy. These can include hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory input, such as being overly sensitive to certain sounds, textures, or smells, or having a high tolerance for pain. Other signs may include difficulty with coordination and motor skills, poor attention and concentration, frequent meltdowns or emotional outbursts, and difficulty with transitions or changes in routine. If a child or individual is experiencing these symptoms and they are impacting their daily life and functioning, it may be beneficial to consider sensory integration therapy.
Sensory integration therapy utilizes a variety of techniques and activities to help individuals with sensory processing disorders. These can include activities that provide deep pressure or proprioceptive input, such as swinging, jumping on a trampoline, or using weighted blankets or vests. Other techniques may involve providing vestibular input through activities like spinning or rocking, or using tactile input through activities like playing with sand or finger painting. The therapy may also incorporate activities that stimulate the visual and auditory senses, such as using light boxes or listening to calming music.
Injury Prevention
The duration and frequency of sensory integration therapy can vary depending on the individual's needs and goals. Typically, therapy sessions may last anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour, and they may be conducted once or twice a week. The duration of therapy can vary as well, with some individuals benefiting from a few months of therapy, while others may require ongoing therapy for a longer period of time. It is important to work with a qualified therapist who can assess the individual's needs and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Sensory integration therapy can offer several potential benefits for individuals with sensory processing disorders. It can help improve sensory processing and integration, leading to better regulation of emotions and behaviors. The therapy can also enhance motor skills and coordination, as well as improve attention and concentration. Strength Training Additionally, sensory integration therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies and self-regulation techniques, allowing them to better navigate and participate in their daily activities and environments.
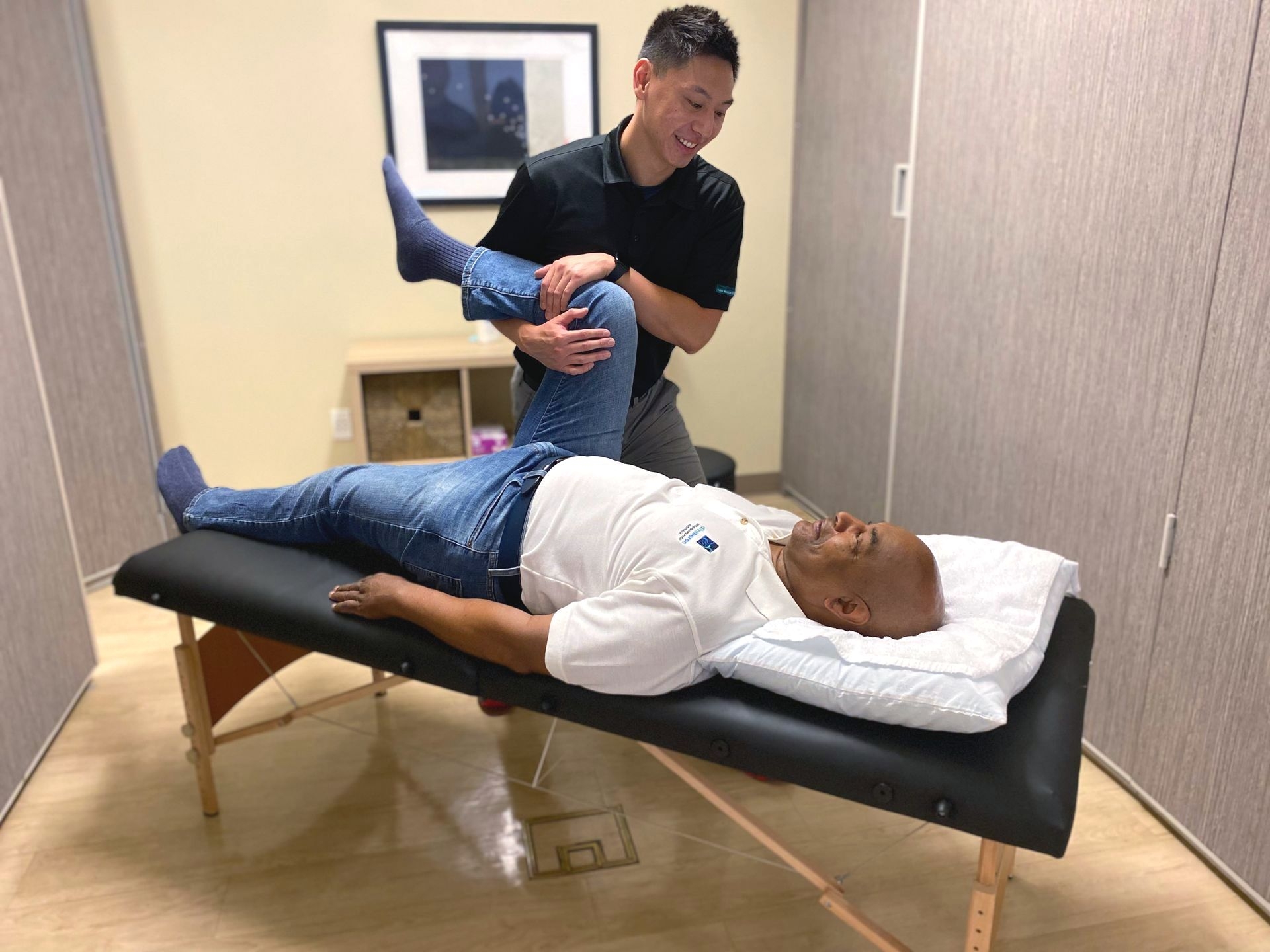
While sensory integration therapy is generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of. Foot Orthotics Assessment Some individuals may find certain sensory activities uncomfortable or overwhelming, and it is important for therapists to carefully monitor and adjust the therapy to ensure the individual's comfort and safety. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or sensory sensitivities may need to avoid or modify certain activities. It is crucial to work with a qualified therapist who can assess the individual's needs and provide appropriate guidance and support.
Parents or caregivers can play a crucial role in supporting and reinforcing the effects of sensory integration therapy at home. They can work closely with the therapist to understand the specific goals and techniques used in therapy, and then incorporate these activities into the individual's daily routine. Neuro-IFRAH Approach This can include providing opportunities for sensory input, such as engaging in sensory play or creating a sensory-friendly environment at home. Parents can also help their child or loved one practice self-regulation techniques and coping strategies learned in therapy, and provide a supportive and understanding environment where the individual feels safe to explore and engage with their senses. Regular communication with the therapist can also help ensure that the therapy goals are being reinforced and progress is being made.

The treatment approaches for quad tendonitis in physical therapy typically involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities. Manual therapy techniques may include soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, and stretching to help reduce pain and improve flexibility. Therapeutic exercises focus on strengthening the quadriceps muscles and improving overall lower extremity stability. This may include exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg presses. Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice or heat therapy may also be used to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper body mechanics and activity modification to prevent further aggravation of the condition.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) is a therapeutic technique used by physical therapists to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. It involves a series of stretching and contracting exercises that target specific muscle groups. PNF works by stimulating the proprioceptors, which are sensory receptors located in the muscles, tendons, and joints. These proprioceptors provide feedback to the brain about the position and movement of the body. By engaging these proprioceptors through PNF exercises, therapists can enhance the communication between the muscles and the nervous system, leading to improved muscle function and overall physical performance. PNF is often used in rehabilitation settings to help patients recover from injuries or surgeries, as well as in sports training to enhance athletic performance.
Physical therapists play a crucial role in addressing spinal cord injury rehabilitation by employing a comprehensive and individualized approach. They utilize a variety of techniques and interventions to promote functional recovery and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with spinal cord injuries. These may include therapeutic exercises, such as range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and balance training, to enhance muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. Additionally, physical therapists may employ gait training and assistive devices to facilitate walking and mobility. They may also utilize modalities such as electrical stimulation, ultrasound, and heat therapy to manage pain and promote tissue healing. Furthermore, physical therapists provide education and guidance on proper body mechanics, postural control, and adaptive strategies to optimize independence and prevent secondary complications. By addressing the unique needs and challenges of each individual, physical therapists play a vital role in facilitating the recovery and rehabilitation process for individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Physical therapy aims to improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase overall physical activity. Through a combination of exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques, physical therapists can help individuals with rheumatoid arthritis improve their range of motion, strengthen their muscles, and enhance their overall quality of life. Additionally, physical therapy can provide education on joint protection techniques and assistive devices, as well as offer guidance on managing pain and fatigue. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of rheumatoid arthritis, helping individuals maintain their independence and improve their overall well-being.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of individuals with lumbar disc herniation. Through a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and education, physical therapists aim to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function. Specific exercises such as lumbar stabilization exercises, McKenzie exercises, and core strengthening exercises help to strengthen the muscles surrounding the lumbar spine, providing stability and support. Manual therapy techniques, including joint mobilization and soft tissue mobilization, can help reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, physical therapists educate individuals on proper body mechanics and ergonomics to prevent further injury and promote long-term spine health. By addressing the underlying causes of lumbar disc herniation and providing individualized treatment plans, physical therapy empowers individuals to regain control of their pain and improve their quality of life.
Physical therapy can be beneficial for individuals with neurological disorders such as multiple system atrophy (MSA). MSA is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects multiple systems in the body, including the autonomic nervous system and motor functions. Physical therapy interventions can help manage the symptoms associated with MSA, such as muscle stiffness, balance and coordination problems, and difficulty with mobility. Therapists can design individualized exercise programs to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, as well as provide gait training and balance exercises to enhance mobility and reduce the risk of falls. Additionally, physical therapists can educate patients and caregivers on energy conservation techniques and assistive devices to optimize functional independence and quality of life. While physical therapy cannot cure MSA, it can play a crucial role in improving overall physical function and enhancing the well-being of individuals living with this neurological disorder.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of individuals who have experienced a stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). The primary goal of physical therapy in stroke rehabilitation is to help patients regain their mobility, strength, and balance. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques and exercises to improve muscle tone, coordination, and range of motion. They may also employ specialized equipment, such as parallel bars or walkers, to assist patients in relearning how to walk and maintain their balance. Additionally, physical therapists work closely with patients to address any pain or discomfort they may be experiencing and provide strategies for managing these symptoms. Through targeted interventions and personalized treatment plans, physical therapy can significantly enhance the functional abilities and overall quality of life for individuals recovering from a stroke.
Yes, physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for individuals with thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). TOS is a condition characterized by compression of the nerves and blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, which is the space between the collarbone and the first rib. Physical therapy interventions for TOS typically focus on improving posture, strengthening the muscles around the thoracic outlet, and increasing flexibility. Specific exercises may include stretching the pectoral muscles, strengthening the scapular stabilizers, and improving overall posture. Additionally, manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization may be used to alleviate pain and improve range of motion. Physical therapy can also provide education on ergonomics and body mechanics to help individuals with TOS manage their symptoms and prevent further aggravation. Overall, physical therapy can play a crucial role in reducing pain, improving function, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with thoracic outlet syndrome.